Measures of Dispersion for Ungrouped Data
41 58 41 54 49 46 52 53 55 52. Random experiments and events Axiomatic approach and addition theorem of probability etc.
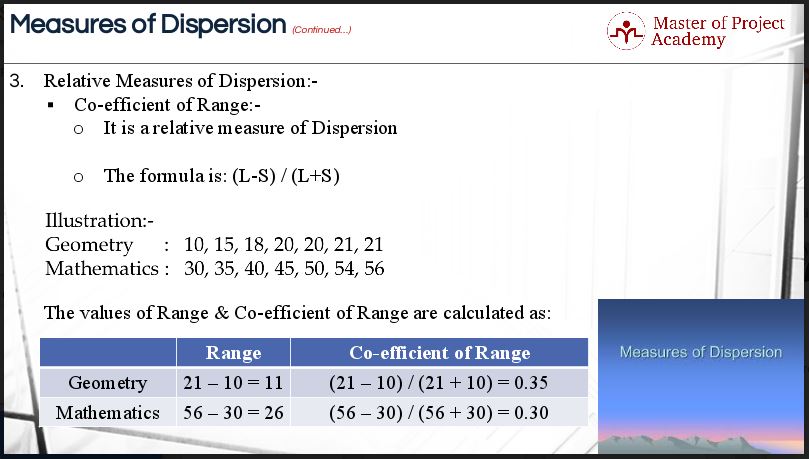
4 Types Of Relative Measures Of Dispersion For Six Sigma
Let us start the MCQs Basic Statistics Quiz.

. Measures of Central Tendency In laymans term a measure of central tendency is an AVERAGE. Range mean deviation variance and standard deviation of ungroupedgrouped data. Lets look at how to determine the Standard Deviation of grouped and ungrouped data as well as the random variables Standard Deviation.
SS f x 2 x for grouped data. The higher is the dispersion or variability of data the larger will be. If the mean of data greater than the median then the data is.
Separate methods are used to represent these two types of data-ungrouped and grouped. N being 11 Q 1 is the size of 3rd value. Median is the most middle value in a set of.
Now let us study the most widely. This quiz contains MCQs about Basic Statistics with answers covering variable and type of variable Measure of central tendency such as mean median mode Weighted mean data and type of data sources of data Measure of Dispersion Variation Standard Deviation Variance Range etc. Linear Inequalities in Two Variables.
Measures of Dispersion for Ungrouped Data. Standard Deviation For Grouped Data. We rely a lot on such measures from analyzing a stock to studying a students performance.
A Right Skewed B Left Skewed C Symmetric D bimodal Q5. Mean median and mode. How many complete dinners can be created from a menu with 3 appetizers 5 soft drinks and 4 desserts if a complete dinner consists of one appetizer one soft drink and one dessert.
Measures of central tendency and location ie. Such concepts find extensive applications in disciplines like finance business accounting etc. The mean average of a data set is found by adding all numbers in the data set and then dividing by the number of values in the set.
We now know about range and mean as measures of dispersion. Operations on Sets. Frequency is nothing but the number of times an event occurs in a given scenario.
For activities NCERT Lab Manual may be referred INTERNAL ASSESSMENT 10 MARKS Periodic Test 5 Marks Mathematics Activities. The mode is the number that appears most frequently in a set of data. Network in Graph Theory.
Standard Deviation simply stated is the measure of the dispersion of a group of data from its meanIn other words it measures how much the observations differ from the central mean. Mean deviation variance and standard deviation of ungroupedgrouped data coefficient of variation analysis of frequency distributions with equal means but different variances. It is the average of all the values given in a set of data.
Range variance and standard deviation. It is a single number of value which can be considered typical in. The median is the middle value when a data set is ordered from least to greatest.
Use the data to make a frequency table. In our example the range of the data is 388. We can find the mode by counting the number of times each value occurs in a data set.
On the other hand if data consists of individual data points it is called ungrouped data. As the values are already arranged in ascending order it can be seen that Q 1 the 3rd value is 29. Usually fo r a data set of 100 to 150 observations the.
Data can be of two types - grouped and ungrouped. Dispersion indicates that the mean is not a good representative of the data set. Measures of Dispersion.
What are the Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion. It measures the absolute variability of a distribution. When data is expressed in the form of class intervals it is known as grouped data.
Sk b Bowleys coefficient of skewness sk b 3 1 3 2 2 1 Q Q Measures of skew ness sk p Pearsons coefficient of skewness sk p S dard Deviation Mean Mode tan Measures of skew ness SS x Sum of Squares SS x 2 x for ungrouped data. All of the above answers are correct. The grouped data computations are used only when a population is being analyzed d.
The grouped data result is more accurate than the ungrouped result c. Hence standard deviation is an important tool used by statisticians to measure how far or how close are the points in a data group from. The measure of dispersion that is influenced most by extreme values is.
The table helps measures the dispersion ie. 1 2 f f x x s for grouped data. Activity file record Term end assessment of one activity Viva.
Statistical Techniques in Business and Economics by Lind Douglaspdf. Modes of Graphical Representation of Data. Measures Of Dispersion.
In statistics the mode is the value that is repeatedly occurring in a given set. MEASURES OF DISPERSION 77 Q 1 is the size of n1 th 4 value. 1st Term Test.
Range Mean deviation Variance and standard deviation of ungroupedgrouped data etc. We know that the data in the form of raw scores is known as ungrouped data and when it is organised into a frequency distribution then it is referred to as grouped data. The measures of location presented in this unit for ungrouped raw data are the mean the median and the.
From the table we can observe the number of times the data appears in the data using frequency. Let us discuss them under separate heads. Of the following observations.
The range is the difference between higher and lower values of the given data. We can also say that the value or number in a data set which has a high frequency or appears more frequently is called mode or modal valueIt is one of the three measures of central tendency apart from mean and medianFor example the mode of the set 3 7 8 8 9 is 8. Graphs of Motion.
20 25 29 30 35 39 41. A measure of dispersion is a quantity that is used to check the variability of data about an average value. A 12 B 60 C 17280 D 30 Q4.
We will first choose a suitable class interval for the above data then we will enter the frequency values to complete the table. The mode is the number that occurs most often in a data set. Measures of Central Tendency MeanMedian and Mode for Ungrouped Data Basic Statistics 2.
None of the above answers is correct. A measure of dispersion is important for statistical analysis. Standard Deviation is the measure of the dispersion of data from its mean.
Ungrouped data Example 1 Calculate range and QD. Number chosen ranges fro m abo ut 5 to 10. While studying economics students should conduct research use relevant data information and facts and understand the economy of their.
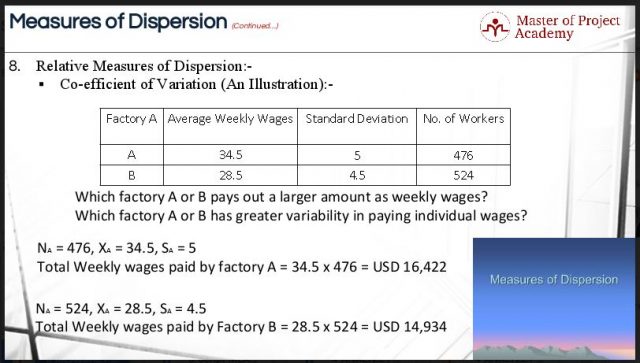
4 Types Of Relative Measures Of Dispersion For Six Sigma
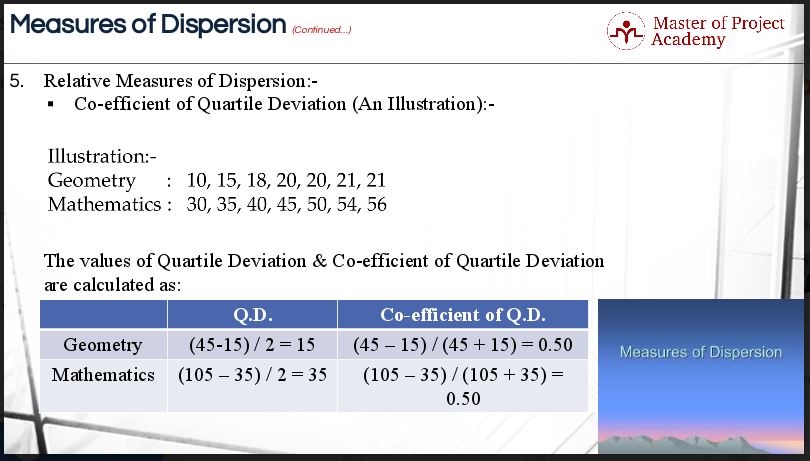
4 Types Of Relative Measures Of Dispersion For Six Sigma

Measures Of Dispersion Of Ungrouped Data

Absolute And Relative Measures Of Dispersion Statistical Methods Measurements Words

Measures Of Dispersion For Ungrouped Data In Frequency Table Variance Method 1 Youtube
Comments
Post a Comment